
This cheat sheet contains notes related to the Pricing and Billing domain of the AWS Cloud practitioner certification and will help you prepare the exam. All of the points covered in these notes are subject to exam questions, so be sure to review them.
About the domain: Pricing & Billing:
this domain covers 16% of the AWS cloud practitioner exam, it targets the following objectives:
- Compare and contrast the various pricing models for AWS.
- Recognize the various account structures in relation to AWS billing and pricing.
- Identify resources available for billing support.
Introduction:
Fundamentals of AWS pricing:
- AWS pricing is similar to how you pay for utilities like water and electricity. You only pay for the services you consume, and once you stop using them, there are no additional costs or termination fees.
- There are three fundamental drivers of cost with AWS: compute, storage, and outbound data transfer.
- there is no charge for inbound data transfer or for data transfer between other AWS services within the same region (There are some exceptions).
- For compute resources, you pay hourly from the time you launch a resource until the time you terminate it unless you have made a reservation for which the cost is agreed upon beforehand.
- For data storage and transfer, you typically pay per GB.
- No minimum commitments or long-term contracts are required unless you choose to save money through a reservation model.
The AWS Free Tier:
AWS Free Tier includes offers that expire 12 months after sign-up and others that never expire.
The following free-tier offers are only available to new AWS customers, and are available for 12 months following your AWS sign-up date:
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2): 750 hours per month of Linux, RHEL, or SLES t2.micro instance usage AND 750 hours per month of Windows t2.micro instance usage (both can be used simultaneously)
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3): 5 GB of Amazon S3 standard storage, 20,000 Get Requests, and 2,000 Put Requests
- Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS): 750 hours of Amazon RDS Single-AZ db.t2.micro Instances for running MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, Oracle BYOL, or SQL Server (running SQL Server Express Edition); 20 GB of database storage; 10 million I/Os; and 20 GB of backup storage.
- Amazon CloudFront: 50 GB Data Transfer Out and 2,000,000 HTTP and HTTPS Requests each month
The following free-tier offers do not automatically expire at the end of your 12-month AWS Free Tier term and are available to all AWS customers:
- AWS DynamoDB: Up to 200 million requests per month (25 Write Capacity units and 25 Read Capacity units); 25 GB of indexed data storage; 2.5 million read requests per month from DynamoDB Streams; ability to deploy DynamoDB Global Tables in up to two AWS regions.
- Amazon Glacier: Retrieve up to 10 GB of your Amazon Glacier data per month for free.
- AWS Lambda: 1 million free requests per month; up to 3.2 million seconds of compute time per
You don’t have to remember all these numbers for the exam, just have an idea about the free tier.
AWS Account Structures & Consolidated Billing for organizations:
AWS Account Structures:
- Accounts act as the main billing entity for AWS Resources.
- accounts are not technically hierarchical, you can use organizational units (OUs) with AWS Organizations to create hierarchical and logical groupings to better manage accounts.
The following account structures are based on common AWS customer organizational, operational, and cost models:
Business Unit Account Structure:

This account structure can be beneficial for customers who want to align their AWS operational and billing controls with individual BUs.
Environment Lifecycle Account Structure:

This account structure can be beneficial for customers who want to align their AWS operational and billing controls with their application deployment lifecycle
Project-Based Account Structure:
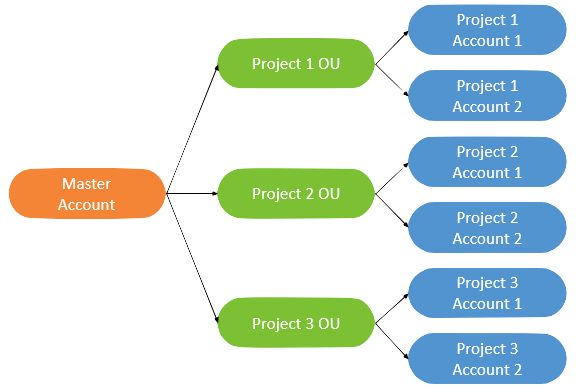
This account structure can be beneficial for customers who want to align their AWS operational and billing controls by product, application workload, or program.
Hybrid AWS Account Structures:

some larger AWS customers find it advantageous to create hybrid combinations that group accounts by multiple dimensions.
Consolidated Billing for Organizations:
Consolidated billing has the following benefits:
- One bill – You get one bill for multiple accounts.
- Easy tracking – You can track the charges across multiple accounts and download the combined cost and usage data.
- Combined usage – You can combine the usage across all accounts in the organization to share the volume pricing discounts, Reserved Instance discounts, and Savings Plans. This can result in a lower charge for your project, department, or company than with individual standalone accounts.
- No extra fee – Consolidated billing is offered at no additional cost.
Pricing details for individual services:
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2):
When you begin to estimate the cost of using Amazon EC2, you need to consider the following:
- Compute: Clock Hours of Server Time, Machine Configuration, Machine Purchase Type, Number of Instances.
- Storage: Additional Storage, Backups, Data Transfer.
- Load Balancing.
- Detailed Monitoring.
- Auto Scaling.
- Elastic IP Addresses: You are charged only if you do not use your elastic IP addresses (Remember this!).
- Operating Systems & Software Packages.
Amazon EC2 pricing models:
AWS On-Demand instances:
- you pay for the compute capacity of the EC2 machine by the hour or second (depending on which instance you run).
- You don’t need any up-front payment to use an on-demand EC2 instance
AWS Reserved Instances:
- you can obtain a significant discount (up to 75%) compared to an on-demand model.
- You can buy a reservation using a range of payment terms including No Upfront, Partial Upfront, or All Upfront.
- To maximize your savings, you can pay all upfront and receive the largest discount.
- There are three RI types:
- Standard RI: Provides the most significant discounts (up to 75% off On-Demand, for steady-state usage.
- Convertible RI: Provides a discount up to 45% off On-Demand instance, you can change Availability Zone, instance size (for Linux OS), networking type, as well as changing instance families, operating system, tenancy, and payment option.
- Scheduled RI: available to launch within the time windows you reserve, allows you to match your capacity reservation to a predictable recurring schedule that only requires a fraction of a day, a week, or a month.
AWS Spot instances:
- represent the unused compute capacity of AWS servers; AWS takes those unused servers and monetizes them to a significant large discount (up to 90% off On-Demand instances).
AWS Dedicated Hosts:
- physical EC2 server fully dedicated to use.
- You can either purchase a dedicated host On-Demand (hourly) or reservation (up to 70% off On-Demand)
AWS Savings Plan: (started on 4 November 2019)
You can read more about this model in this article that we wrote.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3):
When you begin to estimate the cost of Amazon S3, you need to consider the following:
- Storage Class.
- Storage: The number and size of objects stored in your Amazon S3 buckets as well as the type of storage.
- Requests: The number and type of requests.
- Data Transfer: The amount of data transferred out of the Amazon S3 region.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC):
- There is no additional charge for using Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, aside from the normal Amazon EC2 usage charges.
- If you choose to create a NAT gateway in your VPC, you are charged for each “NAT Gateway-hour” that your NAT gateway is provisioned and available.
- If you choose to create a VPN Connection to your VPC using a Virtual Private Gateway, you are charged for each “VPN Connection-hour” that your VPN connection is provisioned and available.
Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS):
When you begin to estimate the cost of Amazon RDS, you need to consider the following:
- Compute: Clock hours of server time, Database characteristics, Database purchase type, Number of database instances.
- Storage: Provisioned Storage, Additional Storage (The amount of backup storage in addition to the provisioned storage amount is billed per gigabyte per month.), Requests, Deployment Type (Single AZ/ Multi-AZ), Data Transfer (inbound is free, outbound is charged).
- License included.
Amazon CloudFront:
When you begin to estimate the cost of Amazon CloudFront, you need to consider the following:
- Traffic Distribution: pricing varies across geographic regions.
- Requests: The number and type of requests (HTTP or HTTPS) made and the geographic region in which the requests are made.
- Data Transfer Out.
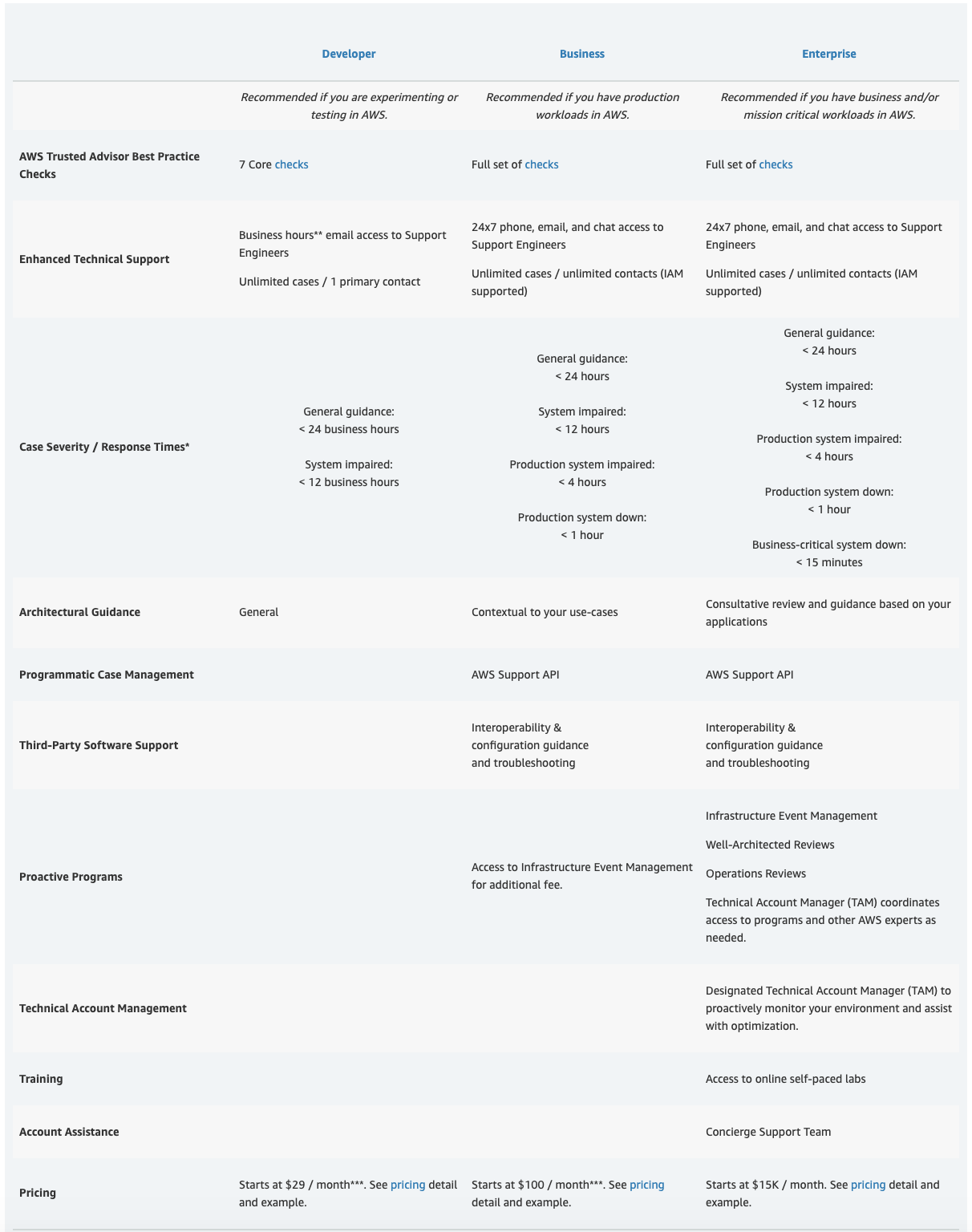
AWS Support Tiers:
AWS provides Four Support tiers and is per AWS Account (except Enterprise):
- Basic:
- Customer Service: one-on-one responses to account and billing questions.
- Support forums.
- Service health checks.
- Documentation, whitepapers, and best-practice guides.
- Developer:
- All the features from Basic Support Tier.
- Best-practice guidance.
- Client-side diagnostic tools.
- Building-block architecture support.
- Business:
- Phone/Email/Chat support with multiple response tiers: General guidance (<24 hours), System impaired (<12 hours), Production system impaired (<4 hours), Production system down (<1 hour)
- All the features from Developer Support Tier.
- Use-case guidance: what AWS products, features, and services to use to best support your specific needs.
- IAM for controlling individuals’ access to AWS Support.
- An API for interacting with Support Center and Trusted Advisor.
- Third-party software support.
- Enterprise :
- less than 15 min response time(business-critical system down), a dedicated Technical Account Manager.
- All the features from Business Support Tier.
- Application architecture guidance.
- Infrastructure event management: short-term engagement with AWS Support to partner.
- AWS Concierge.
- Technical account manager.
- White-glove case routing.
- Management business reviews.
Support plan comparison:
Refer to the table bellow:
AWS cost tools:
TCO calculator:
- TCO calculator allows you to estimate the cost savings when using AWS and provide a detailed set of reports that can be used in executive presentations.
- The calculator gives you the option to modify assumptions that best meet your business needs.
Cost Explorer:
- With Cost Explorer, you can filter graphs by values such as API operation, Availability Zone, AWS service, custom cost allocation tag, Amazon EC2 instance type, purchase option, region, usage type, usage type group, and more.
- you can see a forecast of future costs based on your historical cost data.
- Cost Explorer is a free service.
AWS Budgets:
- track your AWS usage and costs. Budgets use the cost visualization provided by Cost Explorer to show you the status of your budgets, to provide forecasts of your estimated costs, and to track your AWS usage, including your free tier usage.
- You can also use budgets to create Amazon SNS notifications that notify you when you go over your budgeted amounts, or when your estimated costs exceed your budgets.
Cost Allocation Tags:
- Tags can be used to organize AWS resources, and cost allocation tags to track the AWS costs on a detailed level.
- Upon cost allocation tags activation, AWS uses the cost allocation tags to organize the resource costs on the cost allocation report making it easier to categorize and track your AWS costs.
- AWS provides two types of cost allocation tags:
- an AWS-generated tag AWS defines, creates, and applies the AWS-generated tag for you.
- user-defined tags that you define, create.
- Both types of tags must be activated separately before they can appear in Cost Explorer or on a cost allocation report.
AWS Pricing & Billing practice questions:
AWSBOY Cheat sheets:
Notice: we keep updating this material.
You can report a mistake or suggest new notes to add to this AWS Cloud Practitioner Pricing & Billing cheat sheet…let us know in the comment section!
 You need to log in to pass this practice exam.
You need to log in to pass this practice exam.
Hi – Clarification you need to add on the Cheat Sheet for the Business support Tier – there’s a 4 hour response time, 1 hour if you are down.
Thanks,
Jim
Shouldn’t the answer to “pricing model that allows you to bid on unused instance hours” be ‘Reserved’ – I thought that was the only pricing model where you could sell unused capacity on the Reserved Instance Marketplace. Could you please confirm / correct my understanding ?
Hello, here you’ll find the anwser https://www.awsboy.com/aws-ec2-pricing-november-2019/
if we read what you have provided in blogs is that enough for clearing the exam?
we need exam material in the form of mcq’s